Credit Line on UPI: Why Proactive Planning is Key to Success

Contents
- Planning and Assessment Framework
- Assessing Market Size and Target Segments
- Planning Product Features and Underwriting Policies
- Pricing and Competitive Positioning
- Evaluating Technology and Operational Fitment
- Identifying and Mitigating Risk Pockets
- Conclusion
Credit Line on UPI (CLOU) is rapidly emerging as a transformative force in India’s digital credit landscape. As banks increasingly recognize its potential, CLOU stands out as a groundbreaking lending solution poised to address longstanding challenges in credit penetration.
According to Zeta estimates, CLOU has the potential to represent a $1 trillion opportunity for banks by 2030. The substantial revenue potential and the chance to reconceive the design and delivery of traditional lending products are driving banks to be the early adopters in the market.
However, proactive planning and assessment are critical for banks as they navigate the evolving landscape of Credit Line on UPI (CLOU) offerings. By engaging in proactive planning, banks can:
- Effectively gauge the market and evolving regulatory landscape to anticipate its impact on their revenue and profitability
- Establish scalable systems to support future growth rather than being constrained by the limitations of the current technology landscape
- Leverage CLOU as a catalyst to reimagine conventional digital credit products
Planning and Assessment Framework
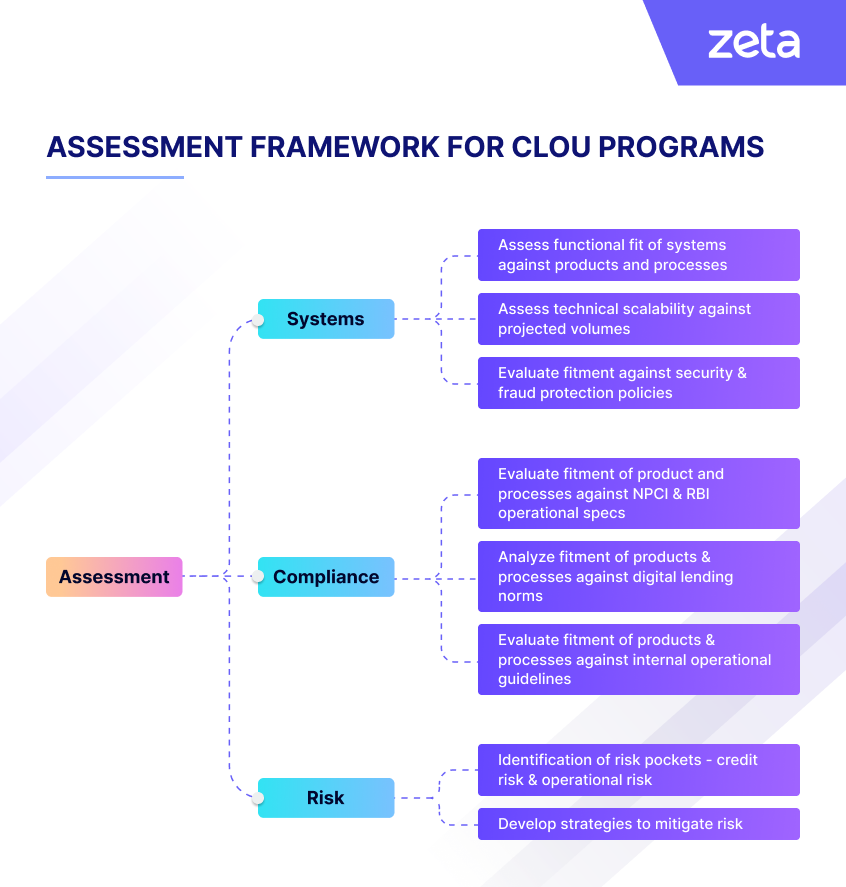
The framework illustrated in images 1 & 2 provides a detailed approach for banks to conduct discovery, planning, and assessment of a CLOU program across key dimensions: market, product, technology stack, compliance, and risk.
Image 1
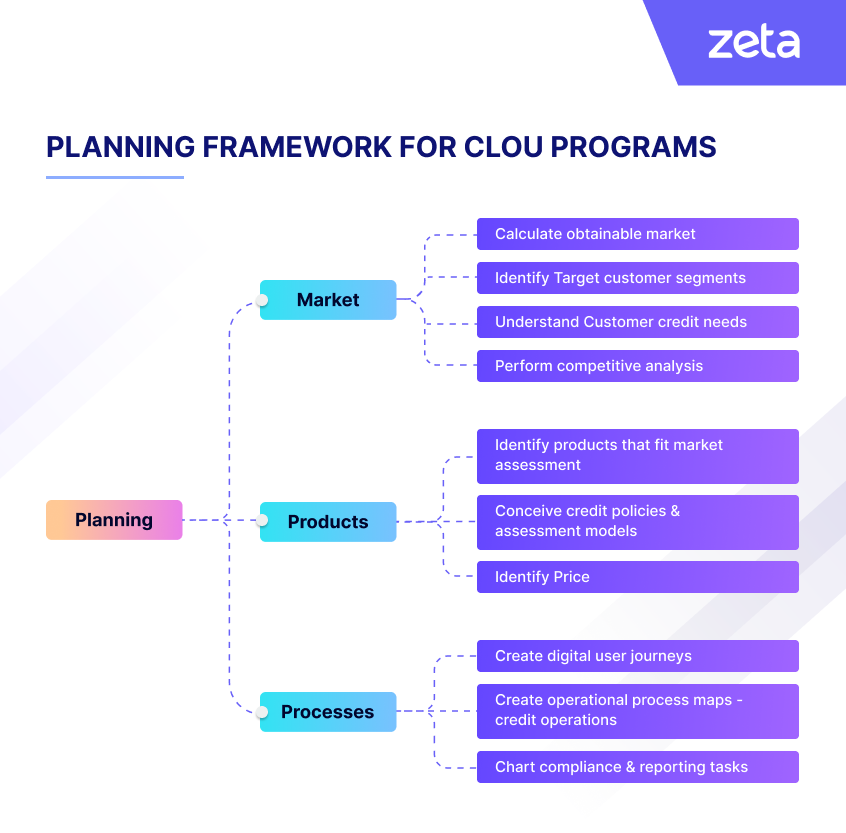
Image 2
You can find the complete adoption framework, including launch and optimization, in our recent white paper Chak De India: Democratizing Credit With Credit Line On UPI.
Assessing Market Size and Target Segments
The first step in planning a CLOU program is to analyze the projected UPI adoption rates for merchant transactions, consumer behavior, and the overall demand for credit products.
- Obtainable Market Size: Understanding the potential market size for CLOU will help banks forecast demand and set realistic goals for the program. Banks should conduct comprehensive market research to estimate:
- Volume of merchant transactions on UPI
- Average transaction value
- Share of credit in fulfilling these transactions
- Average size of the credit line
- New vs Existing customer mix in the portfolio
- Line utilization frequency
- Share of customers revolving beyond interest-free period
- A realistic view of targeted market share.
- Target Customer Segments: Identifying the right customer segments is key to tailoring the credit offering effectively. Banks should segment their customer base based on demographics, transaction patterns, and credit behavior. For instance, tech-savvy millennials who frequently use UPI for transactions might be more inclined to utilize a credit line integrated with UPI.
- Understanding Customer Credit Needs: To design a product that resonates with customers, banks must have a clear understanding of their credit needs. This involves:
- Analyzing credit utilization across existing credit products to identify patterns around size, tenure and type of credit need
- Surveying customers to gauge their interest in CLOU, preferences regarding credit limits and repayment terms, and any additional features they might value
- Competitor Analysis: Understanding the competitive landscape within the context of operating regions, customer segments and products is vital to offering a differentiated CLOU proposition. By analyzing how competitor banks have designed their products and pricing to maximize net revenue (from interest income, interchange, and fees), the bank can refine its own offerings to be more competitive. This insight enables strategic adjustments to maximize profitability, improve customer acquisition, and better align with market demands.
Planning Product Features and Underwriting Policies
Once the market size, target segments, and customer needs are assessed, the next step is to plan the product features and underwriting policies.
- Product Features: CLOU products should be designed to align with insights gained from market analysis, taking into account the historical performance of similar products. Some of the critical dimensions to think about would include:
- Push v/s Pull: Product managers should capitalize on the strengths of UPI to create specialized variations of traditional credit products as on-demand credit solutions.
- Repayment formats: Despite achieving substantial volumes, poor ROI forced several banks to exit interest-free BNPL products in favor of EMI-based products.
- Incentives: To be competitive, CLOU offerings should deliver value akin to credit cards, such as instant provisioning, highly personalized rewards, and merchant-funded offers.
- Underwriting Policies: Developing robust underwriting policies is critical to managing risk while ensuring inclusivity. Banks should leverage various data sources, including granular UPI purchase data, to evaluate creditworthiness. This data can provide insights into spending patterns, income stability, and overall financial behavior, enabling more accurate risk assessment. Policies should take into account the target segment and the risk appetite of the bank.
Pricing and Competitive Positioning
Pricing plays a crucial role in the success of the credit line program. Banks need to consider:
- Competitive Landscape: Evaluate how competitors are pricing similar products. Ensure that the pricing structure for the credit line on UPI is competitive while aligning with the bank’s profitability goals. This includes setting appropriate interest rates, fees, and charges.
- Cost Implications: Factor in the operational costs associated with launching CLOU, ongoing maintenance, and customer service. A well-balanced pricing strategy should cover these costs while offering attractive terms to customers.
- Reimagining Subvention Models: CLOU presents an exciting opportunity to streamline subvention models, enabling banks to innovate their pricing strategies. Unlike traditional personal loans that require merchant partnerships, CLOU leverages UPI’s extensive reach to allow banks to independently set prices for merchant-specific credit lines, without the need for on-ground partnerships and activation.
Evaluating Technology and Operational Fitment
Before implementing the credit line program, banks need to assess the fitment of their existing technology stack and operational processes.
- Technology Stack: The technology infrastructure should support the seamless integration of the credit line with the UPI platform. To successfully launch credit products and utilize CLOU to its full potential, issuers must maintain implementation readiness across six dimensions, as illustrated in image 3.
Image 3

2. Operational Processes: Assessing existing operational processes is crucial for tailoring them to the specific nuances of CLOU. This includes:
- Integrating with backend systems for credit assessment, transaction processing, and customer service.
- Evaluating digital user journeys to ensure they are intuitive and aligned with CLOU’s seamless, real-time experience
- Reviewing and optimizing process maps for credit operations to support the unique aspects of CLOU, such as instant credit provisioning and dynamic transaction management
- Updating compliance and reporting tasks to meet regulatory requirements to ensure accurate, timely reporting
3. Compliance Needs: Assessing systems, products, and processes to meet compliance requirements involves a comprehensive review to ensure alignment with NPCI standards, RBI’s digital lending guidelines, and security and data protection norms. Additionally, internal policies must be integrated to maintain consistency and address any gaps, thereby safeguarding against risks and ensuring regulatory adherence across all operational facets.
Identifying and Mitigating Risk Pockets
Risk management is a critical aspect of launching any new financial product. Banks should:
- Identify Risk Pockets: Conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify potential vulnerabilities. This might include fraud risks, default risks, and operational risks. Analyze historical data and scenario simulations to predict and prepare for possible challenges.
- Develop Mitigation Strategies: Formulate strategies to mitigate identified risks. This might involve implementing advanced fraud detection systems, setting up robust customer verification processes, and establishing clear policies for managing credit defaults.
Conclusion
Launching a Credit Line on UPI program offers significant opportunities for banks to enhance their product offerings and engage with customers in new ways. By evaluating obtainable market, understanding customer needs, designing product features and pricing strategies, developing risk mitigation approaches, and assessing technology and operational fitment, banks can lay a strong foundation for the sustainable growth of their CLOU offerings.
At Zeta, we are dedicated to partnering with banks to bring their Credit Line on UPI programs to life. We look forward to hearing from you and exploring how we can collaborate.