The Issuers’ Guide to Push Tokenization

Contents
Digital payments have changed the way people transact.
Consumers demand speed, security, and convenience, which in turn has made digital wallets increasingly popular. In 2023, they accounted for 50% of e-commerce and 30% of Point of Sale (POS) transactions globally. With the digital payments market projected to grow from $10.09 trillion to $16.63 trillion by 2028, banks have a significant opportunity to lead in this expanding sector.
One of the key assurances digital wallets bring is transaction security. Built around card tokenization capabilities that replace sensitive card data with secure tokens, digital wallets offer reduced fraud and higher protection of cardholder data during transactions.
In our previous blogs on tokenization and mobile tap and pay transactions, we explored the broader concept of securing card transactions with tokenization and how mobile-based digital wallets facilitate contactless payments through tokenized cards. This blog dives into push tokenization and its critical role in further enhancing security and user experience.
What is Push Tokenization
Push provisioning streamlines the process of adding cards to digital wallets or merchant applications, making it easy, quick, safe, and convenient for consumers. Unlike traditional methods where the cardholder initiates the process, push provisioning is initiated by the card issuer. This approach reduces potential errors and enhances security.
Traditionally, to add their cards to a digital wallet, customers need to manually enter card details in the application – such as card number, expiry date, and security code – introducing risks of human error and fraud. Push provisioning eliminates these risks by using secure channels and encryption to transfer card credentials directly to the digital wallet.
Push tokenization flow
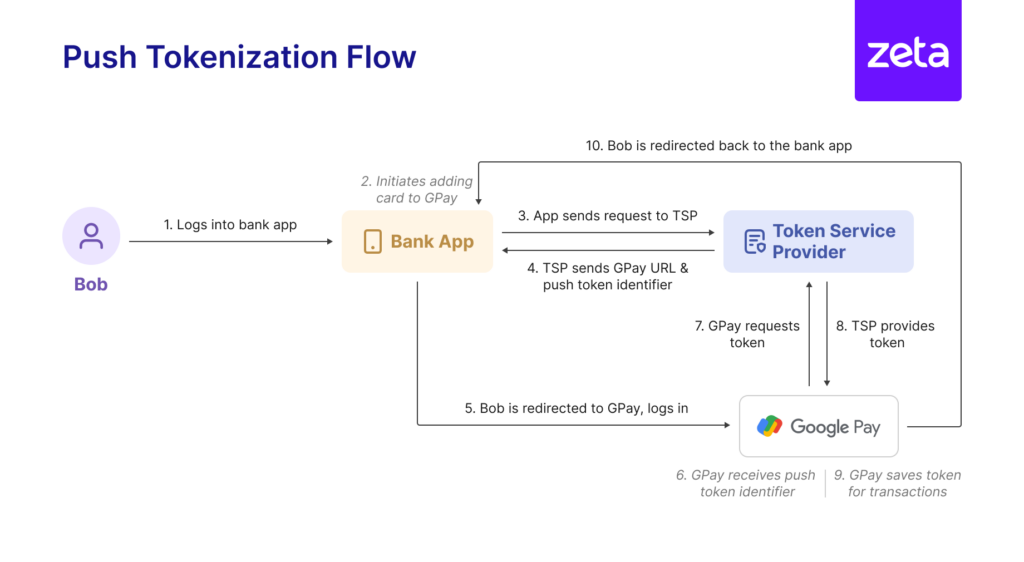
Let’s assume Bob wishes to push his credit card to the Walmart merchant app as well as the Google Pay wallet. Let’s see how he uses his bank’s mobile app to seamlessly push his credit card to the digital wallet first.
Step 1: Initiate Token Push
- Bob logs into his bank’s mobile app, selects his card, and is prompted to choose the merchants and/or wallets to which he wants to push his card.
- Bob selects Google Pay
- The bank’s mobile app forwards Bob’s request to their token service provider (TSP).
- The TSP generates a push token identifier and shares it, along with the Google Pay’s URL, with the bank’s app.
Step 2: Redirect to Merchant
- The bank’s app redirects Bob to the Google Pay app with push token identifier.
- Bob logs into Google Pay.
- Google Pay receives the push token identifier.
Step 3: Token Request and Storage
- The Google Pay app requests the token service provider for a token using the push token identifier.
- The Google Pay app saves the received token to the secure element, allowing Bob to now use it for initiating online as well as tap and pay transactions.
- Bob is redirected back to the bank’s app.
- Bob sees Google Pay added to the list of saved merchants for his card.
Image 1 illustrates this process of push provisioning Bob’s card to his Google Pay wallet.
Image 1
How Issuers Can Enable Push Tokenization
Successfully enabling push tokenization involves a comprehensive approach that encompasses strategic planning, technical integration, and continuous monitoring. Following are the key steps to effectively implement push tokenization:
Partner with a Token Service Provider
The TSP is responsible for generating a secure token, its distribution and management, as well as providing APIs and integration tools so issuers can connect to their systems. Issuers typically partner with technology providers or networks themselves to offer TSP services.
However, not all TSPs currently offer push provisioning capabilities. Issuers thus need to partner with TSPs that offer this capability.
Upgrade payment infrastructure
Issuers’ existing payment infrastructure will need an upgrade to integrate with mobile wallet providers, payment processors, and other essential stakeholders to ensure compatibility and seamless operations across multiple platforms. Issuers will also need to implement secure communication protocols and advanced encryption methods to protect the transmission of sensitive card data to the tokenization service provider, thereby preventing data breaches.
Establish a secure token vault
Issuers need a secure token vault to safely store original card data. This vault should allow retrieval of data when necessary to map back to generated tokens. Managing the vault with top-tier security standards is crucial to prevent unauthorized access and maintain data integrity.
Develop customer communication strategies
When adopting push provisioning of tokenization, issuers need to drive adoption and trust through comprehensive communication to educate cardholders about the advantages of tokenization, including enhanced security and privacy.
Implement continuous monitoring and updates
Continuous monitoring and regular system updates are essential for maintaining the effectiveness of push tokenization. Issuers need to establish robust monitoring systems to quickly detect and respond to potential security threats. Regularly updated tokenization protocols and security measures will help issuers stay ahead of evolving threats and ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
Advantages of Push Tokenization
Push tokenization offers numerous advantages for issuers, transforming the way they handle payment security and customer interactions. By integrating this technology, issuers can unlock several key benefits:
Enhance Security: By replacing sensitive card data with tokens, push tokenization significantly reduces the risk of data breaches and fraud, safeguarding both cardholders and issuers from potential financial losses.
Maintain Regulatory Compliance: This technology helps issuers meet financial regulations like PCI DSS by securely managing data, reducing the risk of fines, and simplifying audits.
Improve User Experience: Push tokenization streamlines transactions across digital platforms, enhancing convenience and fostering customer trust and loyalty.
Improve Cost Efficiency: Reducing fraud and streamlining compliance processes lowers costs, allowing issuers to reinvest savings into growth and innovation.
As digital payments grow, push tokenization is vital for card issuers to offer secure, instant transactions while meeting consumer demands for speed and convenience. This technology positions issuers as leaders in a competitive market. Contact us to learn how Zeta helps issuers prepare for the future of contactless payments.
References:
- Worldpay, The Global Payments Report | 2024
- Payments Dive, Digital wallets to overtake debit cards in stores: report | March 2024
- Fit Small Business, Digital Payment Market Growth & Statistics for 2024 | May 2024



